Acid-Alkaline Balance and Good Health
One of the wonders of human body is homeostasis, which means maintaining biological parameters within narrow
limits. For instance, the pH of blood plasma is kept in the 7.35 - 7.45 range. A drop in pH to 7.1-7.2 is a sign of metabolic acidosis
that can cause significant physiological effects, particularly affecting respiratory and cardiovascular systems. A further drop in pH
to 7.0 or 6.9 sends the body in a downturn spiral that ends in coma and death.
If blood pH is tightly controlled not the same is true for body tissues. An acidic environment in body fluids (other
than blood) and tissues can arise from an acid ash forming diet, toxic overload, emotional stress, lack of rest and other factors.
The term ash refers to that part of the food that remains after food was digested and metabolized (burnt). Vegetables and fruits
leave an "alkaline ash" i.e. metal ions such as potassium, sodium, calcium and magnesium. Proteins, after metabolization leave
an "acid ash" such as the negatively charged ions NO3- (nitrate), SO4
2- (sulfate), PO43- (phosphate), all part of strong acids. So, a diet based mostly on meat
products will eventually lead to health problems (see figure below).
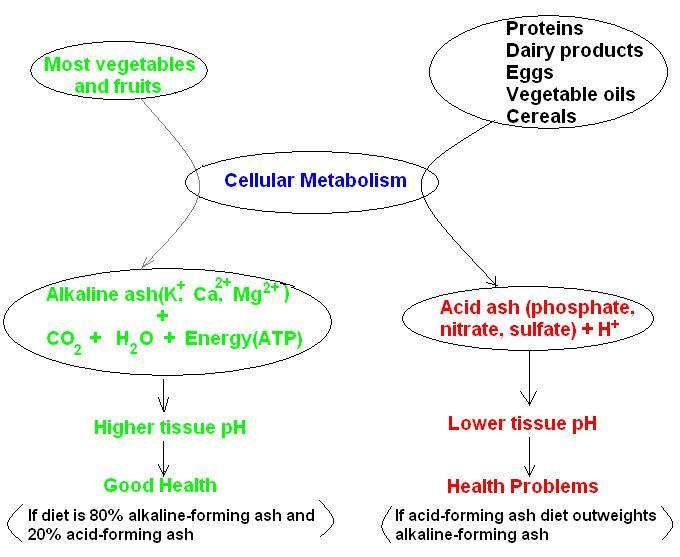
To fight an acidic environment the body will call upon its alkaline reserve that is the alkaline minerals (potassium,
sodium, calcium, magnesium). If the diet does not provide an adequate supply of alkalizing minerals a build-up of acids will result.
The slow deterioration of body functions can go undetected for many years before clinical signs become apparent. By then
correcting the damage done is much harder to achieve. Mild acidosis, as it is common in many people consuming an animal protein
based diet can lead to:
- cardiovascular damage that includes:
- depression of myocardial contractility
- sympathetic overactivity, which includes tachycardia, vasoconstriction, decreased arrhythmia threshold
- peripheral arteriolar vasodilatation
- vasoconstriction of peripheral veins
- effects of hyperkalaemia (increased plasma potassium) on heart
- respiratory problems:
- hyperventilation: this is a compensatory response
- shift of oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve to the right (decreased affinity of hemoglobin for oygen)
- other pathological conditions:
- increased bone resorption (in chronic acidosis)
- bladder and kidney conditions, including kidney stones
- weight gain, obesity and diabetes
- rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis
- gout
- immune deficiency
- low energy and chronic fatigue
- premature aging
In the table below (adapted from website: www.i-amperfectlyhealthy.com/) you have a list of alkaline ash-forming foods and acid ash-forming foods. By choosing your foods so that 80% are alkaline ash forming and 20% acid ash forming you ensure that your body is in good health.
|
Alkaline ash-forming foods |
|
VEGETABLES
Garlic
Asparagus
Fermented
veggies
Watercress
Beets
Broccoli
Brussel
sprouts
Cabbage
Carrot
Cauliflower
Celery
Chard
Chlorella
Collard
greens
Cucumber
Eggplant
Kale
Kohlrabi
Lettuce
Mushrooms
Mustard
greens
Dulce
Dandelions
Edible flowers
Onions
Parsnips (high
glycemic)
Peas
Peppers
Pumpkin
Rutabaga
Sea
veggies
Spirulina
Sprouts
Squashes
Alfalfa
Barley
grass
Wheat grass
Wild greens
Nightshade veggies
|
FRUITS
Apple
Apricot
Avocado
Banana
(high glycemic)
Cantaloupe
Cherries
Currants
Dates/Figs
Grapes
Grapefruit
Lime
Honydew melon
Nectarine
Orange
Lemon
Peach
Pear
Pineapple
Berries (all)
Tangerine
Tomato
Tropical fruits
Watermelon
PROTEIN
Eggs
(poached)
Whey protein powder
Cottage cheese
Chicken
breast
Yogurt
Almonds
Chestnuts
Tofu
(fermented)
Flax seeds
Pumpkin seeds
Tempeh (fermented)
Squash
seeds
Sunflower seeds
Millet
Sprouted seeds
Nuts |
OTHER
Apple
cider vinegar
Bee pollen
Lecithin granules
Probiotic cultures
Green
juices
Veggies juices
Fresh fruit juice
Organic milk
(unpasteurized)
Mineral
water
Alkaline antioxidant water
Green tea
Herbal tea
Dandelion tea
Ginseng
tea
Banchi tea
Kombucha tea
SWEETENERS
Stevia
Ki
sweet
SPICES/SEASONINGS
Cinnamon
Curry
Ginger
Mustard
Chili
pepper
Sea salt
Miso
Tamari
All herbs
ORIENTAL
VEGETABLES
Maitake
Daikon
Dandelion
root
Shitake
Kombu
Reishi
Nori
Umeboshi
Wakame
Sea
veggies |
|
|
Acid ash-forming foods |
|
FATS
& OILS
Avocado
oil
Canola oil
Corn oil
Hemp seed oil
Flax oil
Lard
Olive oil
Safflower
oil
Sesame oil
Sunflower oil
FRUITS
Cranberries
GRAINS
Rice cakes
Wheat
cakes
Amaranth
Barley
Buckwheat
Corn
Oats
(rolled)
Quinoa
Rice
(all)
Rye
Spelt
Kamut
Wheat
Hemp seed flour
DAIRY
Cheese,
cow
Cheese, goat
Cheese, processed
Cheese, sheep
Milk
Butter
|
NUTS
& BUTTERS
Cashews
Brazil
nuts
Peanuts
Peanut butter
Pecans
Tahini
Walnuts
ANIMAL
PROTEIN
Beef
Carp
Clams
Fish
Lamb
Lobster
Mussels
Oyster
Pork
Rabbit
Salmon
Shrimp
Scallops
Tuna
Turkey
Venison
PASTA
(WHITE)
Noodles
Macaroni
Spaghetti
OTHER
Distilled vinegar
Wheat germ
Potatoes |
DRUGS
& CHEMICALS
Aspartame
Chemical drugs
Medicinal drugs Psychedelic drugs
Pesticides
Herbicides
ALCOHOL
Beer
Spirits
Hard
liquor
Wine
BEANS
& LEGUMES
Black
beans
Chick peas
Green peas
Kidney beans
Lentils
Lima beans
Pinto
beans
Red beans
Soy beans
Soy milk
White beans
Rice milk
Almond milk
|
|
But how do we know the pH status in body fluids? By measuring the pH in two body secretions, i.e. saliva and urine
we get a pretty good idea about the acidity or alkalinity of our body tissues and internal fluids. This is done by using pH paper strips
to determine the pH in saliva and urine. If the morning urinary pH fluctuates between 6.0 and 6.5 and 6.5 and 7.0 in the evening the
body is within a healthy range. The pH of saliva should be 6.5-7.5 all day for someone in a healthy state. The measurements should
be performed one hour before a meal or two hours after a meal. A pH reading below 6.0 indicates that you should pay immediate
attention to your diet by modifying it accordingly as discussed above.
It is interesting to note that only now have nutritionists started to pay attention to what enlightened physicians like
Dr. William Howard Hay said as early as 1933 about all diseases being a state of autotoxication or self poisoning caused by a
build-up of acidic end products of cellular metabolism. His far reaching ideas are now, 70 years later, recognized as valid and worthy
to be heeded. Thus, a recent nutritional epidemiology report presented evidence that a cysteine and methionine rich protein diet has
a negative effect on bone mineral density (1). If not used for protein synthesis these sulfur-containing amino acids leave an acid ash
(sulfate) upon metabolic degradation. In order to buffer this acidic environment the bone will release calcium and magnesium so it
becomes demineralized and in the long run this can lead to osteoporosis and other complications.
|