|
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
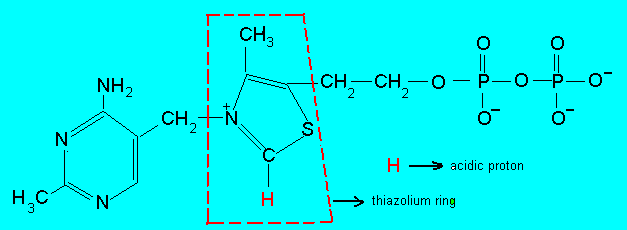
|
Thiamine pyrophosphate (the coenzyme form of vitamin B1). The thiazolium ring is the moiety involved in the catalytic process.
|
|
Some of the reactions in which TPP is involved are listed below: 1. Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) is one of the coenzymes required by the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex for the decarboxylation of pyruvate: pyruvate + CoA-SH + NAD+ ----> acetyl-CoA + CO2 + NADH 2. TPP is also required in the degradation of branched-chain amino acids isoleucine, leucine and valine. The second stage in this process is catalyzed by a-ketoisovalerate dehydrogenase, a multienzyme complex that employs the coenzymes TPP, FAD, NAD+ and the lipoamide. 3. TPP is involved in a reaction of the pentose phosphate pathway, i.e.in the formation of sedoheptulose-7-phosphate. The enzyme that catalyzes this reaction (transketolase) requires TPP as coenzyme. The pentose phosphate pathway is one of the generators of reducing power (NADPH) necessary for biosynthetic processes as well as for several reductive processes, such as the regeneration of GSH in the erythrocytes whose function is to protect the integrity of cell membrane by removing the hydrogen peroxide and lipid hydroperoxides through the reaction catalyzed by GSH-peroxidase. |
|
References 1. Dudeja, P.K. et al. (2001) Am.J.Physiol. Cell Physiol. 281: C786-C792. Mechanism of thiamine uptake by human jejunal brush-border membrane vesicles. 2. Rindi, G. and Laforenza, U. (2000) Proc.Soc.Exp.Med. 224(4) 246-255. Thiamine intestinal transport and related issues: recent aspects. 3. Meador, K.J. et al. (1993) Ann.Neurol. 34(5), 724-726. Evidence for a central cholinergic effect of high-dose thiamine. |
